When it comes to food packaging, the right material can make all the difference. From preserving freshness to ensuring safety and sustainability, packaging plays a vital role in food products’ journey from manufacturers to consumers. Understanding the different materials used in food packaging can help both businesses and consumers make smarter choices, focusing on durability, environmental impact, and product quality.
Common Materials Used in Food Packaging
Food packaging materials come in many forms, each suited to different needs. These materials can generally be categorized into plastics, paper, glass, metals, and biodegradable options. Let’s dive into the pros and cons of each.
1. Plastics
Plastics are by far the most commonly used materials for food packaging. They’re lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for a wide variety of food products.
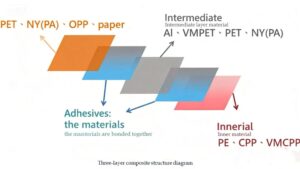
- Polyethylene (PE): This plastic is used in grocery bags, plastic wraps, and bottles. It’s resistant to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for packaging liquids, frozen foods, and meats.
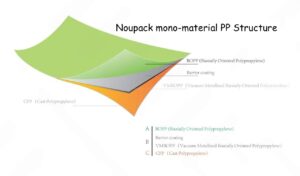
- Polypropylene (PP): Known for its high melting point, PP is used in packaging hot food, microwaveable trays, and yogurt cups. It’s strong, flexible, and durable.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Often used for beverages, PET is transparent, lightweight, and offers excellent oxygen and moisture barriers. It’s a common choice for soft drink and bottled water packaging.
- Polystyrene (PS): This plastic is used in disposable containers, cups, and cutlery. Though it’s a popular option, environmental concerns have led to a decline in its use.
- Bioplastics: With a push for sustainability, bioplastics made from renewable sources (like corn or sugarcane) are gaining popularity. Materials like PLA (Polylactic Acid) are used in packaging fresh produce, snacks, and even ready-to-eat meals.
2. Paper and Cardboard
Paper and cardboard are eco-friendly materials that are increasingly popular for food packaging, especially for businesses looking to reduce their plastic use. They’re biodegradable, recyclable, and renewable.
- Corrugated Cardboard: This durable material is used for bulk food packaging, such as cereals and frozen goods. It provides strength and protection during transit.
- Paperboard: Used for snack boxes, juice cartons, and take-out packaging, paperboard is versatile, lightweight, and can be coated for extra protection against moisture.
- Wax-Coated Paper: Ideal for greasy foods like sandwiches or pastries, wax-coated paper prevents moisture and oil from seeping through and compromising the food’s quality.
- Kraft Paper: Known for its natural look, kraft paper is used in organic and eco-friendly food packaging. It’s sturdy, recyclable, and biodegradable, which makes it an appealing choice for environmentally conscious brands.
3. Glass
Glass is an old but reliable packaging material, especially for products like sauces, jams, pickles, and beverages. Glass is non-reactive, which means it doesn’t alter the taste or quality of food.
- Advantages: Glass containers provide excellent protection against oxygen, moisture, and light, which helps preserve food freshness. It’s also fully recyclable, offering a sustainable option.
- Disadvantages: Glass is heavier than plastic and can break easily, making it less suitable for some types of food products, particularly those requiring heavy handling or transportation.
4. Metals
Metal packaging is most commonly seen in canned goods, including vegetables, soups, and ready meals. Metals such as aluminum and steel offer excellent protection and preservation.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and durable, aluminum is used in beverage cans, foil wraps, and lids. It has a strong barrier to oxygen and light, making it perfect for extending the shelf life of packaged food. It is also highly recyclable.
- Steel: Steel is commonly used in food cans, particularly for more robust items like beans and meat. It’s strong, offers a good protective layer, and helps preserve the food for a long time.
- Advantages: Both aluminum and steel provide excellent protection, helping keep food fresh for extended periods. Plus, they’re both highly recyclable, making them environmentally friendly options.
- Disadvantages: Metal packaging is heavier than alternatives like plastic, and while it’s recyclable, the process is more complex than plastic recycling.
5. Biodegradable and Compostable Materials
With growing environmental concerns, there’s a push towards biodegradable and compostable packaging. These materials break down naturally in the environment, making them a sustainable option for eco-conscious businesses and consumers.
- Plant-Based Plastics: Made from renewable resources such as corn or sugarcane, these plastics are more eco-friendly than traditional petroleum-based plastics. They’re used for food packaging items like fresh produce and snacks.
- Mushroom Packaging: An innovative material made from mycelium, mushroom packaging is fully compostable and can be used for certain food products. While still a niche product, it’s gaining popularity in sustainable packaging circles.
- Edible Packaging: Some companies are experimenting with edible packaging made from ingredients like seaweed or rice. This type of packaging could eliminate the need for disposal entirely, making it a revolutionary step toward sustainability.
Choosing the Right Packaging Material
The ideal material for food packaging depends on several factors, including product type, shelf life, environmental impact, and cost. Here are some things to consider when making your choice:
- Product Type: Different food products require different types of packaging. For instance, dry foods like cereal and snacks may be best in plastic or paper, while liquid foods like beverages need bottles or cartons that provide moisture protection, such as PET or glass.
- Shelf Life Requirements: Foods with a longer shelf life, such as canned goods, require packaging that provides a strong barrier against oxygen and moisture. For fresh produce, biodegradable or breathable packaging may be more appropriate.
- Environmental Impact: As sustainability becomes a key concern, many businesses are opting for recyclable, biodegradable, or compostable packaging. Materials like paper, bioplastics, and glass can all offer eco-friendly benefits.
- Cost: The cost of packaging materials is always an important factor. While premium materials like glass or metal may provide better protection, they can be more expensive than plastics or paper-based alternatives.
- Convenience: Packaging should also align with consumer needs. Easy-to-open packages, resealable bags, and lightweight containers can greatly improve the consumer experience, especially for on-the-go products.
Choosing the right material for food packaging involves balancing factors like protection, cost, shelf life, and environmental impact. Plastics, paper, glass, metals, and biodegradable materials all have their advantages, and the ideal choice will vary depending on the product. With sustainability becoming a key concern, the food packaging industry is evolving to offer more eco-friendly alternatives.
Ultimately, businesses must consider their product’s needs, their consumer base, and environmental impact when selecting packaging materials. By understanding the options available, you can make smarter, more sustainable decisions that benefit both your business and the planet.