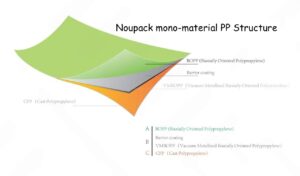
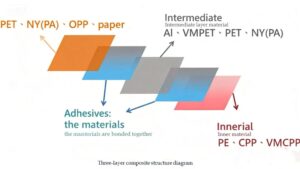
Food processing and packaging play crucial roles in ensuring that food products reach consumers in a safe and desirable state. From the moment raw materials are harvested to when they arrive on store shelves, there are multiple steps involved to ensure that food maintains its nutritional value, freshness, and safety.
Primary Food Processing
Primary food processing refers to the initial steps taken to prepare raw agricultural products for consumption or further refinement. This stage includes:
- Cleaning: Removing dirt, debris, and potential contaminants from raw ingredients like grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Sorting and Grading: Ensuring uniformity in size, quality, and color before further processing.
- Preservation: Techniques such as freezing, drying, and salting are used to extend the shelf life of fresh produce.
These primary processes lay the foundation for the next stages of food handling, maintaining both safety and quality.
Secondary Food Processing
Secondary food processing involves turning these raw, cleaned materials into more complex food products. Common methods include:
- Cooking: Heat is applied to kill bacteria and improve texture and taste.
- Fermentation: Microorganisms are used to enhance flavor and increase shelf life, as seen in products like yogurt, cheese, and beer.
- Canning and Bottling: Foods are preserved in airtight containers to prevent spoilage over long periods. This is often done with fruits, vegetables, sauces, and soups.
At this stage, food undergoes more intricate processes that transform raw materials into market-ready products.
Advanced Food Processing Techniques
With advancements in technology, modern food processing uses more sophisticated methods to ensure food safety and enhance product appeal. These methods include:
- Pasteurization: A heat treatment process that destroys pathogens while preserving the flavor of liquids like milk and juice.
- Vacuum Sealing: Removing air from the packaging to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life.
- Freeze-Drying: This process freezes food and removes moisture under a vacuum, producing lightweight, shelf-stable items like instant coffee or dried fruits.
Advanced techniques make it possible to create highly durable food products that retain their taste and nutritional value for longer periods, meeting the needs of today’s fast-paced lifestyles.
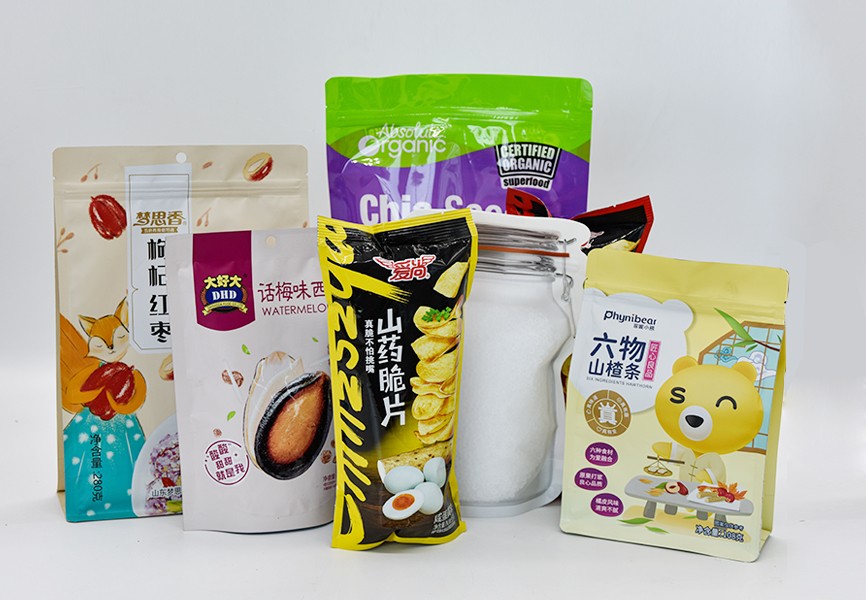

The Role of Packaging in Food Processing
Food packaging is as important as the processing itself. It not only keeps food safe from external contaminants but also helps in maintaining the texture, flavor, and appearance of the product over time. Packaging fulfills several essential functions:
- Protection: Packaging materials such as glass, plastic, and cardboard shield food from air, moisture, and microorganisms that cause spoilage.
- Convenience: Ready-to-eat meals, resealable packages, and easy-to-open containers cater to the growing demand for convenience in modern life.
- Marketing and Branding: Attractive packaging designs with clear labels play a crucial role in catching the consumer’s eye and communicating key product information, such as nutritional value, ingredients, and expiration dates.
The role of packaging goes beyond just containment—it impacts the consumer’s experience and influences their purchasing decisions.
Sustainable Trends in Food Processing and Packaging
With growing consumer awareness about environmental issues, the food industry is seeing a shift toward sustainable processing and packaging methods. Key trends include:
- Eco-friendly Packaging: Biodegradable and recyclable materials are being adopted to reduce waste and carbon footprint.
- Energy-efficient Processing: Companies are investing in technologies that lower energy consumption during processing, such as solar-powered equipment and water-saving devices.
- Minimal Processing: As demand for fresh, organic foods rises, producers are employing minimal processing methods that preserve natural flavors and nutrients while still ensuring safety.
These sustainable practices help reduce the environmental impact of food production while appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
Final Thoughts
The scope of food processing and packaging is vast, encompassing a broad range of techniques that ensure food remains safe, nutritious, and appealing from the time it’s harvested until it reaches consumers. Whether through primary processing or advanced packaging innovations, these practices continue to evolve, meeting the challenges of modern-day consumption trends and environmental concerns.