In recent years, flexible packaging has gained significant traction in various industries, from food and beverages to pharmaceuticals and consumer goods. This rise in popularity is due to the numerous advantages flexible packaging offers, such as its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. But what exactly are the requirements for flexible packaging? In this blog, we will break down the key factors that contribute to the success of flexible packaging and explore the essential elements that packaging manufacturers and brands must consider when choosing the right packaging solutions.
What is Flexible Packaging?
Flexible packaging refers to packaging materials that are made from non-rigid materials like plastic, foil, paper, and films. These materials allow for flexibility, as opposed to rigid packaging such as glass or metal. Flexible packaging is commonly used for items such as snack foods, beverages, cosmetics, and medical products. The materials are designed to be lightweight, durable, and adaptable, offering various benefits for both producers and consumers alike.
Key Requirements for Flexible Packaging
- Durability and Protection
The primary function of any packaging is to protect the contents. For flexible packaging, durability is a crucial requirement. It must ensure that the product remains intact throughout the supply chain, from production to distribution to consumer use. Flexible packaging must be resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, light, oxygen, and contaminants that could compromise the quality and safety of the product inside.
For example, when packaging food products, flexible packaging must prevent the ingress of moisture and oxygen to keep food fresh for extended periods. This is typically achieved through the use of barrier films that prevent the entry of oxygen and moisture. In the case of pharmaceuticals or medical products, packaging must meet strict hygiene standards to avoid contamination.
- Printability and Branding
Branding plays a critical role in the success of any product, and flexible packaging offers excellent opportunities for high-quality graphics and printing. Packaging must be able to display vibrant, accurate colors and designs to capture consumer attention and communicate brand identity effectively.
Flexo printing, gravure printing, and digital printing are commonly used for flexible packaging, each offering unique advantages. Print quality and the ability to maintain consistent colors throughout a run are vital to ensuring that the brand’s image is effectively conveyed. Packaging must also be able to accommodate the necessary labeling information, such as ingredient lists, usage instructions, and regulatory requirements.

- Sustainability and Environmental Impact
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is an increasing demand for sustainable packaging options. Flexible packaging is no exception. Brands are under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint and create packaging that is recyclable, compostable, or made from recycled materials.
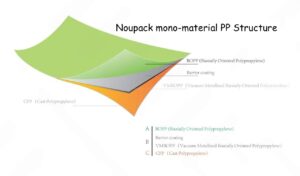
The use of materials like polyethylene, which is widely used in flexible packaging, can be a double-edged sword. While it offers excellent barrier properties, it also poses challenges in terms of recyclability. Packaging companies are continuously innovating to produce eco-friendly solutions, such as biodegradable films, recyclable mono-materials, and the use of renewable resources.
Brands are now considering packaging designs that allow consumers to easily recycle or reuse the materials. This is especially important in industries such as food and beverage, where packaging waste is a significant concern. Therefore, manufacturers need to align with the latest industry standards for recyclability and sustainability, which are ever-evolving.
- Cost-Effectiveness
Flexible packaging is known for being more cost-effective compared to traditional rigid packaging. This is particularly important for brands looking to reduce production and shipping costs. Flexible packaging often requires fewer materials and is lighter, resulting in lower transportation costs.
In addition, flexible packaging allows for the efficient use of materials. For example, flexible pouches use less material than rigid plastic or glass containers. This means brands can save on material costs while reducing their overall environmental impact. With flexible packaging, manufacturers also benefit from faster production speeds and less waste, further driving down costs.
However, there is a balance between cost and quality. Companies need to ensure that the packaging they select is cost-effective while still meeting durability, aesthetic, and regulatory requirements.
- Shelf Life and Product Freshness
Flexible packaging must be able to extend the shelf life of the product. This is particularly relevant for perishable goods like snacks, ready-to-eat meals, and beverages. To achieve this, packaging materials are often designed to provide an effective barrier against external factors such as moisture, air, and light. Vacuum-sealing and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) are common techniques used to preserve the freshness and quality of the product.
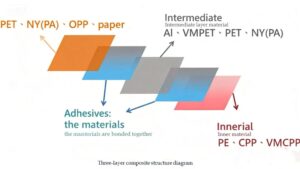
For example, a snack food package might use a multi-layer laminate structure that includes a foil layer for barrier properties, ensuring the product stays crisp and fresh. Similarly, packaging for beverages may include a layer of foil to protect against light and oxygen, which could cause the beverage to spoil.

The shelf life is a critical factor in product packaging, especially when considering the logistical challenges of distribution. Flexible packaging must be engineered to protect products and maintain freshness during the entire journey from the manufacturer to the consumer.
- Convenience and Ease of Use
One of the main advantages of flexible packaging is its convenience. Consumers today are increasingly looking for packaging that is easy to open, resealable, and portable. Flexible packaging can be designed to feature zippers, easy-tear notches, spouts, or stand-up pouches that provide convenience during use.
For example, pouches with resealable zippers offer the consumer the ability to keep the product fresh after opening. This type of packaging is commonly used for snacks, pet food, and other products that require frequent opening and closing. Similarly, spouted pouches, commonly seen in liquid packaging, offer easy pouring with no mess.
Convenience is a significant selling point for consumers, and flexible packaging companies must design packages that meet these demands.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Flexible packaging must also comply with relevant industry regulations and standards. For food packaging, this means ensuring that the materials used are food-safe and meet FDA guidelines. For medical or pharmaceutical products, packaging must meet strict quality and safety standards to ensure the product remains sterile and uncontaminated.
Packaging companies must stay abreast of local and international regulations to avoid penalties and ensure that their products meet the required safety and quality standards.
Conclusion: Meeting the Demands of Modern Packaging
Flexible packaging is an essential part of the global packaging industry, and its demand is expected to continue growing. However, to succeed in this competitive market, manufacturers must carefully consider various factors that contribute to the effectiveness of flexible packaging. These include durability, printability, sustainability, cost-effectiveness, shelf life, convenience, and regulatory compliance.
For brands, choosing the right flexible packaging solution is a delicate balance between innovation, consumer preference, and cost-efficiency. By meeting these requirements, flexible packaging manufacturers can ensure their products stand out on the shelves while delivering exceptional performance and value.
Key Takeaway: The Essential Requirements for Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging requires a combination of durability, sustainability, printability, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with industry regulations. By meeting these demands, manufacturers can produce packaging that not only protects products but also enhances consumer experience and aligns with evolving environmental goals. With these essential factors in mind, the future of flexible packaging looks promising and ready to meet the needs of a wide variety of industries.