Flexible packaging materials are essential for keeping food products fresh, safe, and visually appealing, offering brands a variety of options to meet specific needs. With the food industry’s emphasis on quality and sustainability, choosing the right flexible packaging is crucial for both product preservation and consumer appeal. This guide covers the main types of flexible packaging materials, their benefits, and what food brands should consider when selecting them.
Why Flexible Packaging is Essential for Food Products
Flexible packaging has become increasingly popular in the food industry because of its adaptability, lightweight structure, and ability to protect food from spoilage. Unlike rigid containers, flexible packaging conforms to various product shapes and sizes, allowing for efficient storage and easy transportation. It also offers multiple options for finishes, closures, and sizes, making it ideal for everything from snacks and ready-to-eat meals to frozen foods.
Flexible packaging is engineered to offer protection against light, moisture, and air, helping to extend the shelf life of perishable goods. This advantage not only reduces food waste but also helps maintain flavor and quality from production to the point of consumption.
Types of Flexible Packaging Materials for Food
Different types of flexible packaging materials offer unique benefits depending on the product’s requirements. Here’s an overview of some of the most common materials used for food packaging:
1. Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is one of the most commonly used materials in flexible food packaging. It’s durable, flexible, and cost-effective, making it ideal for a wide range of food applications, including fresh produce, frozen items, and baked goods. PE packaging can be made clear or opaque, allowing for customization based on product and branding needs.
Polyethylene provides excellent moisture resistance, which is essential for products that need protection against humidity or freezer burn. Additionally, it is recyclable, which is an added benefit for brands focused on sustainability.
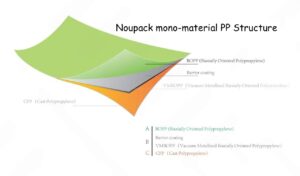
2. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is known for its strength and resistance to oils, chemicals, and high temperatures, making it a preferred choice for snack foods, dried foods, and microwavable items. PP is also highly transparent, enhancing product visibility—a major plus for consumers who like to see what they’re purchasing.
Brands often use PP for food packaging because of its lightweight properties, which help reduce shipping costs. Additionally, PP offers good printability, which allows brands to create eye-catching designs and maintain their visual identity on retail shelves.
3. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate, or PET, is a strong, lightweight material widely used in packaging for items like chips, snacks, and sauces. PET’s main advantage is its ability to serve as an oxygen barrier, which is critical for products that need a longer shelf life without the use of preservatives.
This material is also resistant to moisture and temperature, which makes it suitable for both refrigerated and ambient products. PET is highly recyclable, aligning with the growing demand for environmentally friendly packaging solutions. With the addition of metallized layers, PET can also block light, further enhancing its protective capabilities.
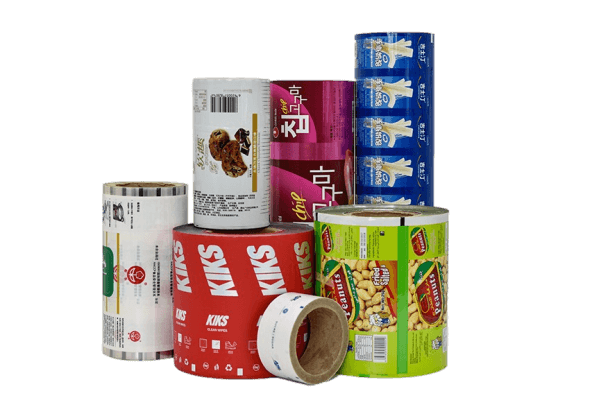

4. Aluminum Foil
Aluminum foil is a popular choice for flexible packaging, especially for products that are highly sensitive to light, moisture, and oxygen. Foil pouches are often used for items like coffee, dairy products, and processed foods, where maintaining freshness and flavor is a priority.
Aluminum’s barrier properties are exceptional, providing one of the best protections available for food packaging. However, it’s often combined with other materials to improve durability and reduce the overall weight of the package. While not as environmentally friendly on its own, foil packaging can be part of a recyclable composite material, enhancing its appeal for eco-conscious brands.
5. Biodegradable and Compostable Films
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, biodegradable and compostable films are gaining traction in the food industry. Made from plant-based materials like PLA (polylactic acid) and cellulose, these films offer a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics. They’re especially popular for packaging organic and natural products, where consumers value environmental responsibility.
Biodegradable films provide decent moisture barriers but are generally not as durable as conventional plastics. While they may have limitations in terms of strength and flexibility, they meet the needs of brands committed to reducing their environmental impact.
Benefits of Flexible Packaging Materials for Food Products
Flexible packaging offers multiple advantages for food manufacturers and consumers alike. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Extended Shelf Life and Freshness
With barrier properties that protect against oxygen, moisture, and light, flexible packaging helps extend the shelf life of perishable foods. By keeping contaminants out, flexible packaging preserves the flavor, texture, and nutritional value of food products, which is essential for consumer satisfaction.
2. Cost-Efficiency and Lightweight Structure
Flexible packaging materials are generally lighter than rigid containers, reducing shipping costs and the amount of fuel needed for transportation. This lightweight structure also makes flexible packaging easier to store and handle, making it a cost-effective solution for food manufacturers and retailers.
3. Customizable and Consumer-Friendly Designs
Flexible packaging can be customized with resealable zippers, spouts, tear notches, and other consumer-friendly features that enhance convenience. Resealable zippers, for instance, allow consumers to keep food fresh after opening, reducing waste. These design options are especially useful for snack foods, coffee, and other products that may be consumed over time.
4. Sustainable Options to Meet Environmental Goals
With the rise in eco-conscious consumers, flexible packaging materials offer sustainable options such as recyclable PE, PET, and biodegradable films. Brands that adopt sustainable packaging can appeal to environmentally aware shoppers, helping to build a positive brand image and meet regulatory standards for sustainable practices.
5. Enhanced Visual Appeal and Brand Recognition
Flexible packaging offers excellent print quality, allowing brands to display vibrant colors, logos, and product details that stand out on store shelves. From transparent windows that showcase product quality to full-color printing that attracts attention, flexible packaging plays a crucial role in building brand recognition and influencing purchase decisions.
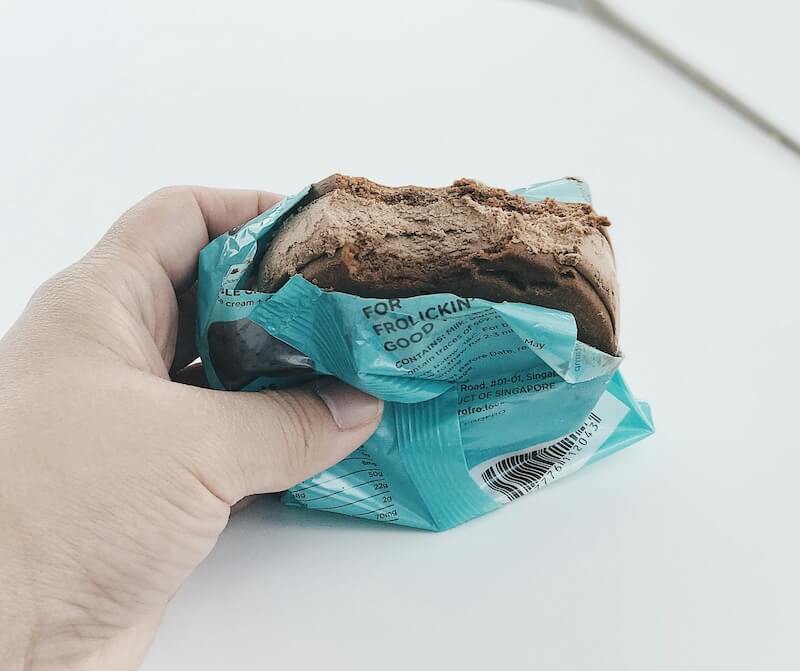

Choosing the Right Flexible Packaging Material for Your Food Product
Selecting the right flexible packaging material involves balancing product protection, cost, sustainability, and branding needs. Here are some important factors to consider:
1. Understand Your Product’s Sensitivity
Every food product has specific preservation needs. For instance, products sensitive to moisture will benefit from PE’s moisture resistance, while those needing oxygen barriers may perform better in PET or foil. Determine the factors that affect your product’s freshness, such as exposure to air or light, to choose the right packaging material.
2. Consider the Environmental Impact
More consumers are choosing brands that prioritize eco-friendly practices. If sustainability is important to your brand, consider biodegradable, compostable, or recyclable materials. These options help reduce environmental impact and resonate with environmentally conscious consumers.
3. Evaluate Packaging Costs and Scalability
Cost is a crucial factor for food brands, especially for small to medium-sized businesses. Evaluate the costs of each packaging material and assess whether it fits your budget and production scale. Lightweight, flexible materials often reduce costs in the long run due to their lower shipping and storage needs.
4. Choose a Consumer-Friendly Design
Flexible packaging can be tailored with convenient features like resealable closures, easy-open notches, and pour spouts. Think about how consumers will use the product and incorporate design elements that make the experience more enjoyable and practical.
5. Work with a Trusted Supplier
To ensure high-quality packaging, work with a reputable supplier experienced in flexible packaging for food products. A good supplier can provide material samples, help you navigate environmental regulations, and suggest options that meet both your product’s needs and your brand’s vision.
Conclusion
Flexible packaging materials offer food brands a range of options for preserving product quality, enhancing convenience, and meeting sustainability goals. Whether it’s polyethylene for moisture protection, PET for long shelf life, or biodegradable films for eco-friendly appeal, the right flexible packaging material can make all the difference in consumer satisfaction and brand reputation. By understanding the features and benefits of each material, food brands can select packaging that best suits their products and business goals.