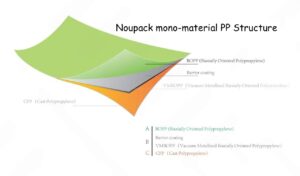
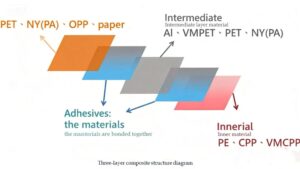
Choosing the right laminating film is essential for protecting and enhancing printed materials, ensuring durability, and achieving the ideal look. Whether you’re laminating business documents, educational materials, or signage, the type and quality of laminating film can make a significant difference in the final product’s appearance and lifespan. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about selecting laminating film, including types, thickness, finishes, and the key factors to consider for different projects.
Why Laminating Film Matters
Laminating film provides a protective layer over documents, graphics, and signage, making them more durable and resistant to damage from handling, moisture, or fading. This layer can also enhance the visual appeal, giving materials a polished look that draws attention. However, not all laminating films are created equal—different films offer distinct benefits and are suited to different types of projects.
For example, some laminating films are best for indoor applications where flexibility and clarity are important, while others are ideal for outdoor use, offering UV resistance and durability. Choosing the right film can save you from costly replacements and ensure that your laminated materials meet specific aesthetic and functional needs.
Key Types of Laminating Film
To choose the right laminating film, it’s helpful to understand the main types available and what they offer.
1. Thermal Laminating Film
Thermal laminating film uses heat to create a bond with the document, making it durable and secure. It’s commonly used for high-volume applications such as business cards, menus, and large signage. Thermal laminating films come in both glossy and matte finishes, offering versatility in appearance. Due to their strength and longevity, they are well-suited for items that will be handled frequently or displayed long-term.

2. Cold Laminating Film
Cold laminating film doesn’t require heat, making it ideal for sensitive materials that might be damaged by high temperatures, such as certain photos or inkjet prints. It is often used for quick or delicate projects and is also suitable for large format applications where heat may be impractical. Cold lamination can be useful for environments where temperature-sensitive graphics need protection without risking damage.
3. Pressure-Sensitive Film
Similar to cold laminating film, pressure-sensitive film bonds with the material when pressed firmly, without any need for heat. It’s particularly useful for items like decals and signs that can’t be exposed to high temperatures. Pressure-sensitive film is often a preferred choice for projects requiring durability and fast application, as it’s easy to use and provides good protection.
4. Specialty Laminating Films
Specialty films come with additional features like UV resistance, anti-graffiti coatings, or even anti-microbial properties, which are increasingly popular for public displays and restaurant menus. These films tend to be more expensive but are beneficial for materials that will be exposed to harsh elements or frequent handling. Specialty laminates are a smart choice for applications like outdoor signage, medical facilities, or high-traffic public areas.
Choosing the Right Film Thickness
Film thickness is an essential consideration because it impacts the rigidity, durability, and feel of the laminated product. Laminating film thickness is usually measured in mils, with each mil equating to 0.001 inches.
- 1.5 to 3 mils: Ideal for flexible materials like posters, maps, or indoor signage. This thickness provides a basic level of protection without compromising flexibility.
- 5 mils: Adds some rigidity, making it suitable for documents that will be frequently handled but still need some flexibility, such as menus and instructional materials.
- 7 to 10 mils: Offers maximum protection and a highly rigid structure, making it best for items like badges, outdoor signs, and ID cards that require robust durability.
When choosing thickness, think about the environment in which the laminated item will be used. For instance, outdoor signs benefit from thicker films for added durability, while a thinner laminate may work fine for temporary or indoor materials.
Glossy vs. Matte Finish
The finish you choose can have a significant impact on both the appearance and functionality of your laminated materials. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
- Glossy Finish: Glossy laminating film makes colors and images pop, adding vibrancy to printed materials. This high-shine look is ideal for promotional items, photographs, and any materials that need a visually striking presentation. However, gloss can cause glare, which may be distracting in bright environments.
- Matte Finish: Matte film reduces glare and offers a softer, more professional appearance. It’s great for text-heavy documents, instructional materials, and anything that needs to be easily readable under different lighting conditions. Matte finishes also resist fingerprints and smudges, making them a popular choice for frequently handled items.
- Textured Finish: This option is less common but adds a unique tactile quality to materials, often making them easier to grip and handle. Textured finishes are commonly used for business cards, high-end menus, and specialty signage.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Laminating Film
Choosing the right laminating film involves more than just picking a type and thickness. Here are a few other factors to consider:
1. Project Purpose
Start by identifying the primary purpose of the laminated material. For instance, will it be displayed outdoors, where it might be exposed to sunlight and weather? Or will it be used indoors and need a high-quality, glossy finish? Understanding the purpose helps narrow down the type, thickness, and finish that best meets your needs.
2. Budget
Different types of laminating film come at various price points, so consider your budget before making a choice. Thermal laminating film is typically affordable and great for bulk projects, while specialty films, like UV-resistant or anti-microbial options, come at a premium. If durability and longevity are key, investing in a higher-quality film may save money on replacements down the line.
3. Application Method
Consider whether you have access to a thermal or cold laminating machine, as this will impact which film types are suitable. If you only have a cold laminator, for instance, thermal films won’t work. Additionally, if your laminator has specific size or thickness limits, be sure to choose film within those specifications.
4. Environmental Factors
Where the laminated product will be used also influences your choice. For example, laminating film with UV resistance is essential for outdoor signage, as it prevents fading from sunlight. Similarly, anti-graffiti laminates are helpful in high-traffic, public areas.

Testing Laminating Film for Specific Needs
Before committing to a large quantity of laminating film, consider ordering samples to test on your actual materials. This can help you confirm the durability, appearance, and tactile qualities before making a larger investment. Testing is especially important for specialty films, where the unique qualities may be hard to gauge without seeing them firsthand.
Tips for Working with Laminating Film
Getting the best results from laminating film also involves using it correctly. Here are a few tips:
- Align Materials Carefully: Before laminating, make sure your materials are aligned to avoid misplacement.
- Choose Appropriate Temperatures: For thermal lamination, make sure your laminator is set to the correct temperature based on the film’s specifications. Overheating can lead to bubbling or curling, while too low of a temperature may result in an incomplete bond.
- Allow Time for Cooling: Let laminated items cool completely before handling or cutting to prevent warping.
- Store Film Properly: Store laminating film rolls or pouches in a cool, dry place to prevent warping or damage. Avoid humid areas, as moisture can affect the film’s adhesive properties.
Conclusion
Choosing the right laminating film requires careful consideration of the project’s needs, from durability and flexibility to finish and environmental exposure. By understanding your options and selecting the right type, thickness, and finish, you can create laminated materials that are both functional and visually appealing.
Whether you need a flexible finish for menus or a UV-resistant layer for outdoor signage, selecting the right laminating film can help your materials last longer and look their best.