The global push for sustainability has made biodegradable packaging solutions a top priority for brands. These materials offer the promise of a reduced environmental footprint, but navigating the options requires a deep understanding of their material performance and cost implications. This is not a simple choice between plastic and paper. It’s a complex decision that involves balancing product protection, shelf life, and brand messaging with the realities of manufacturing and consumer behavior. This article will explore the key considerations and innovations that are shaping this evolving industry.
E-Commerce Ready Packaging Design: Meeting Digital Marketplace Requirements and Consumer Expectations
For brands that sell products online, a different set of rules applies to packaging. E-commerce ready packaging design must withstand the rigors of shipping and handling while also providing a memorable unboxing experience. This means the packaging needs to be durable enough to protect the product without excessive use of fillers. It also needs to be visually appealing, as the package is the first physical interaction a customer has with a brand. This design must meet both the practical requirements of the digital marketplace and the high aesthetic expectations of modern consumers.
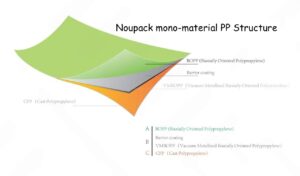
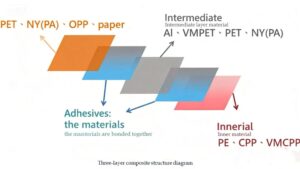
For many products, a single layer of packaging is not enough. Advanced material combinations are required to create a package with superior barrier performance. This is particularly true for items sensitive to oxygen, moisture, or light. A multi-layer film might combine a biodegradable plastic with a natural barrier coating. While these combinations may perform well in laboratory testing, their performance in real-world applications can vary due to temperature fluctuations, humidity, and handling. Brands must conduct extensive testing to ensure their chosen materials hold up under all conditions.

Climate-Specific Packaging Solutions: Adapting Barrier Properties for Varying Temperature and Humidity Environments
Climate is a key factor in packaging design. Climate-specific packaging solutions are engineered to adapt their barrier properties to varying temperature and humidity environments. For example, a package designed for a dry, cool climate will have different moisture barrier needs than one designed for a hot, humid one. This requires a nuanced approach to material selection and construction, ensuring the product remains fresh regardless of where it is shipped or sold.
In a crowded retail space, a package has only a few seconds to capture a consumer’s attention. Visual hierarchy in packaging design is the scientific approach to arranging design elements to guide the consumer’s eye. This involves making key information—like the brand name and product type—the most prominent, while secondary information is given less visual weight. By using techniques like font size, color contrast, and strategic placement, brands can create a package that is not only visually appealing but also easy to understand and navigate.
Active and Intelligent Packaging: Next-Generation Solutions for Food Preservation and Quality Monitoring
The future of packaging is not just about containment; it’s about active protection and data. Active and intelligent packaging incorporates components that perform a function beyond simple containment. For example, a package might have an oxygen scavenger to extend shelf life or a time-temperature indicator that changes color if the product has been exposed to improper conditions. These next-generation solutions are transforming food preservation and quality monitoring, providing a new level of safety and transparency for both brands and consumers.
For luxury brands, the feel of the package is as important as its appearance. Premium packaging printing techniques such as embossing, debossing, foil stamping, and matte or gloss finishes can elevate a product’s perceived value. A cost-benefit analysis of these specialized finishes and effects is necessary to determine their value. While they add to the unit cost, they can also justify a higher price point and create a stronger brand identity, which can lead to a significant return on investment.
Smart Manufacturing in Packaging Industry: IoT Integration and Production Efficiency Optimization
The smart manufacturing revolution is transforming the packaging industry. IoT integration allows machines to communicate with each other and with a central system, providing real-time data on production. This data can be used to identify bottlenecks, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production schedules. This leads to a significant increase in production efficiency, reduces waste, and allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands. Some products simply don’t fit into a standard box or pouch. Specialty product packaging requires unique engineering solutions to accommodate unusual shapes, weights, and preservation requirements. This could involve creating a custom-molded tray for a delicate item or a multi-chamber pouch for a product with multiple components. These custom-engineered solutions ensure that every product, no matter how unusual, can be safely and securely packaged.
Active Packaging Innovations: Integrating Antimicrobial Properties with Traditional Barrier Functions
In the fight against spoilage and contamination, active packaging innovations are a game-changer. These solutions go beyond simple barriers by integrating antimicrobial properties directly into the packaging material. By releasing small amounts of natural antimicrobial agents, the package can inhibit the growth of bacteria and mold, extending the product’s shelf life. This is particularly useful for fresh food products and is a key area of research for future food safety.
Modern consumers want to know the story behind their products. Narrative-driven packaging uses a package as a canvas to communicate brand values and product origins. This could include a simple, heartfelt message from the founder, a small graphic showing the sourcing of the ingredients, or a QR code that links to a video of the product being made. This technique creates a deeper connection with the consumer and builds brand loyalty.
International Standards for Food-Contact Packaging: Requirements, Testing and Documentation
For brands with a global presence, navigating the myriad of international standards for food-contact packaging is a complex but necessary task. Each region has its own specific requirements, testing, and documentation protocols to ensure the safety of the materials. Brands must be meticulous in their compliance, as a failure to meet these standards can lead to product recalls, legal issues, and a damaged reputation.
With thousands of products vying for attention on a shelf, a package needs to stand out. Stand-out packaging design uses visual techniques to capture attention in competitive retail spaces. This could include a bold use of color, an unusual shape, or a clever graphic that tells a story. The goal is to create a design that is not just aesthetically pleasing but also instantly recognizable and impossible to ignore.
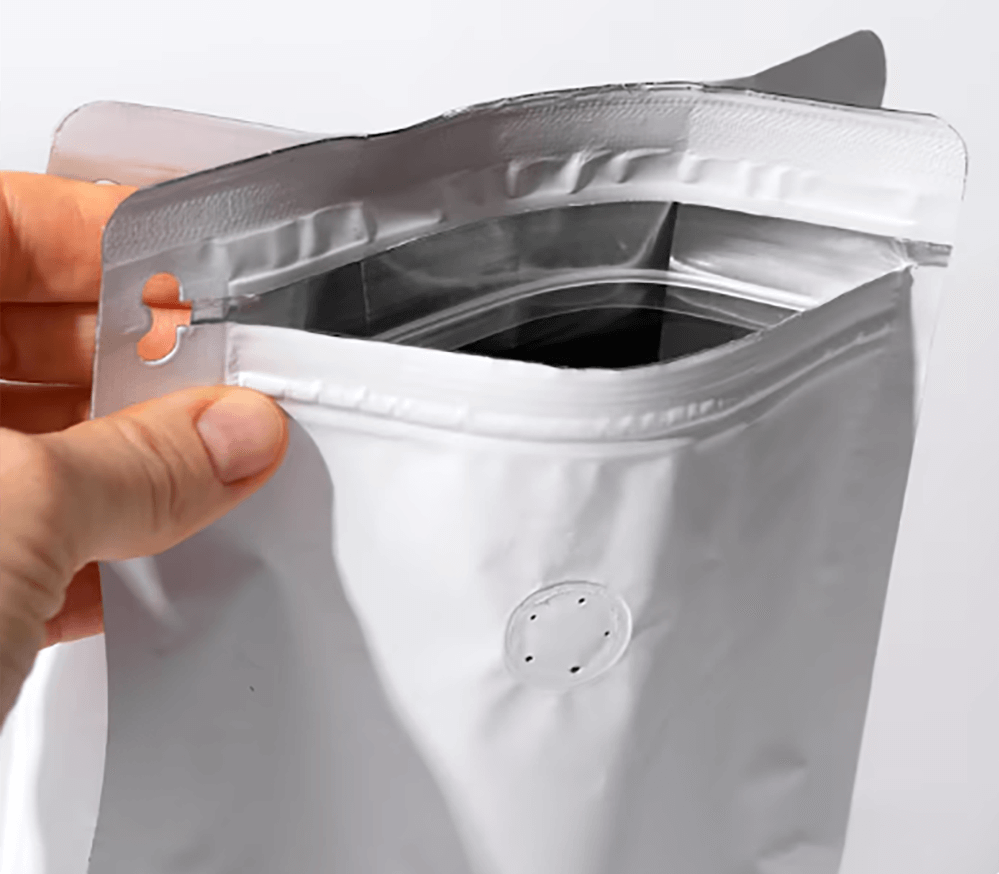

Ergonomic Considerations in Flexible Packaging: Opening, Dispensing and Resealing Innovations
A package that is difficult to open or use can lead to consumer frustration. Ergonomic considerations in flexible packaging focus on making the package as user-friendly as possible. This includes opening, dispensing, and resealing innovations like easy-to-use zippers, tear notches, and pour spouts. By paying attention to these small details, brands can enhance the consumer experience and build a reputation for quality and convenience.
Environmental responsibility also means reducing material use. Lightweight packaging engineering is the science of minimizing material usage while maintaining product protection. This involves using advanced materials that are thinner but just as strong as traditional materials and optimizing the package shape to use as little material as possible. This approach not only reduces waste but also lowers shipping costs, providing a double benefit for brands.
Ensuring Food Safety Through Advanced Packaging Materials: Scientific Testing and Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring food safety is the most critical function of packaging. This requires the use of advanced packaging materials that can create a barrier against contaminants and pathogens. Scientific testing is used to verify that the materials meet all safety standards, and rigorous regulatory compliance ensures that they are approved for food contact. Brands must be vigilant in this area to protect their consumers and their reputation.
Some of the most innovative packaging solutions come from solving the most difficult problems. Technical solutions for complex packaging requirements often serve as case studies in material and process innovation. These stories, whether they involve creating a package for a highly reactive substance or one that needs to be used in an extreme environment, provide valuable lessons and inspiration for the entire industry. They show that with the right combination of engineering and creativity, any packaging challenge can be overcome.