The most common materials used in flexible snack packaging include a variety of plastics, paper, and aluminum, each offering unique properties that enhance product preservation and consumer appeal. Here’s a breakdown of these materials:
- Plastic Films
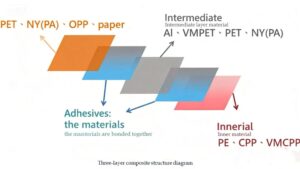
- Polyethylene (PE): Widely used for its flexibility and heat sealability, PE serves as the inner layer in many flexible packages. It is non-reactive and can withstand high acidity, making it suitable for various food applications.
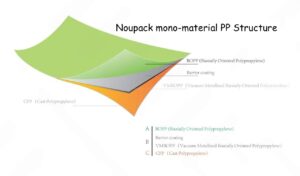
- Polypropylene (PP): Known for its higher melting point compared to other plastics, PP is often used in applications requiring durability and resistance to heat. It can also be produced in matte finishes for aesthetic purposes.
- Polyester (PET): PET is favored for its excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, making it ideal for extending the shelf life of snacks. It is also lightweight and has good dimensional stability.
- Nylon: Often used in laminations, nylon enhances barrier strength and puncture resistance, making it suitable for vacuum-sealed products.
- Aluminum Foil
Aluminum foil provides a superior barrier against moisture, light, and oxygen, which is crucial for maintaining the freshness of snacks. It is commonly used in multi-layer laminates to create a protective layer that helps extend shelf life while also being recyclable .
- Bioplastics
Bioplastics are increasingly being adopted due to their environmentally friendly properties. They effectively prevent air, grease, and oils from penetrating the packaging, making them suitable for snack foods like chips and baked goods .
- Paper
While not as common as plastics or foil in flexible snack packaging, paper can be used in combination with other materials to enhance sustainability. Kraft paper, for example, is known for its strength and can be utilized in multiwall bags or as part of a composite structure .
- Metalized Films
Metalized films combine plastic with a thin layer of metal (usually aluminum) to improve barrier properties while remaining lightweight. These films are often used in snack packaging to protect against light and moisture while providing a shiny appearance that appeals to consumers .
Conclusion
In summary, the flexible snack packaging industry primarily utilizes various types of plastics (such as PE, PP, PET, and nylon), aluminum foil, bioplastics, paper, and metalized films. Each material plays a critical role in ensuring product freshness, extending shelf life, and meeting consumer preferences for convenience and sustainability. As the industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on using recyclable and sustainable materials to align with consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions.